CARPentry Modeling Environment (CME)
Welcome to the CARPentry modeling environment documentation. CARPentry provides a set of tools for modeling electrophysiological, mechanical and fluidic aspects of cardiac function. CARPentry comprises a set of tools for specific applications:
- bench: bench is a simple tool for solving, analyzing and tuning of models of cellular dynamics.
- carpentry: carpentry is a swiss army knife for electro-mechano-fluidic modeling of cardiac function at the tissue and organ scale.
- pre- and post-processing tools: CARPentry comprises a set of additional auxiliary executables to deal with specific pre-processing tasks such as generating meshes, assigning fiber architecture, find the initial state of a tissue model or compute solutions of various PDEs, and with post-processing tasks for analyzing computed scalar, vector or tensor fields.
- visualization tools and interfaces: CARPentry provides various solutions for visualization of simulation results at the single cell scale (limpetGUI) and tissue scale (meshalyzer) and provides interfaces to powerful and versatile general purpose visualization tools such as ParaView.
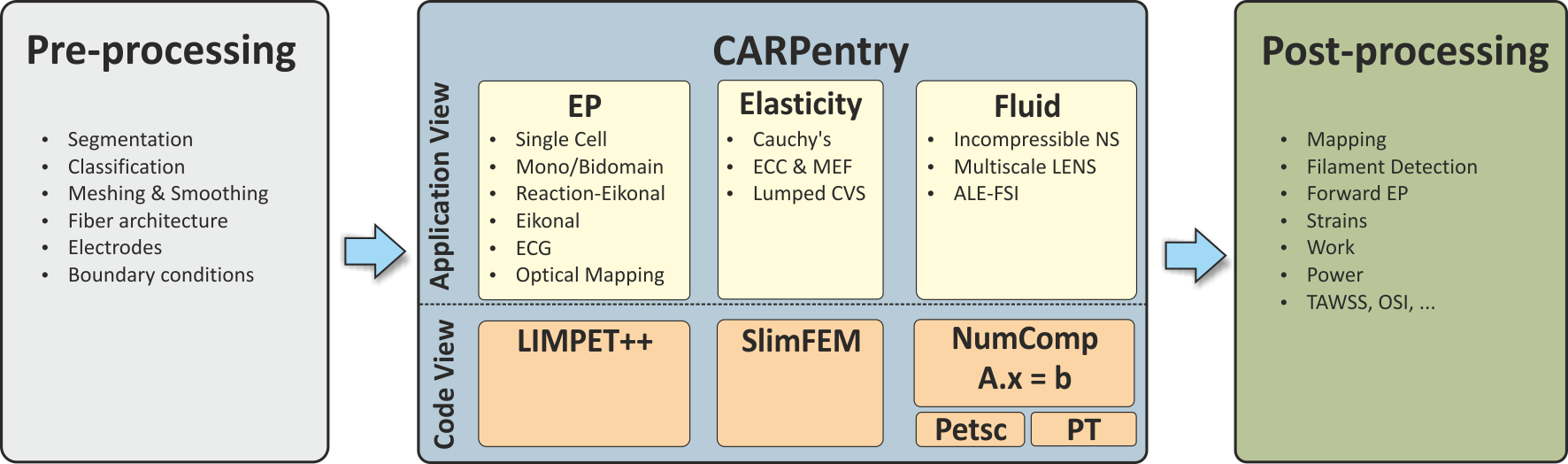
Fig. 1 Technically, the CME structure comprises the shown components: A) pre-processing tools, B) simulator core components, C) parameterization and initialization engine and D) post-processing tools.
Essentially, there are two distinct ways of using CARPentry:
- plain mode: In plain mode all executables are used directly. This is the recommended mode of usage for simpler single physics experiments up to a medium degree of complexity. Typically, such simpler experiments are run directly from the command line or, with increasing complexity, simple scripts are built to better organize the modeling workflow. For highly complex multiphysics organ scale simulations this approach is not recommended as managing the configuration of experiments becomes quickly intractable and error-prone.
- carputils mode: For complex experiments involving more than one physics or studies which investigate a larger parameter space it is recommended to use carputils to design an in silico experiment. carputils provides a wide range of python functionality for setting up, running, and postprocessing the results of CARPentry simulations. A guide explaining how to install and run simulations, as well as define your own examples and tests is given in the carputils documentation.
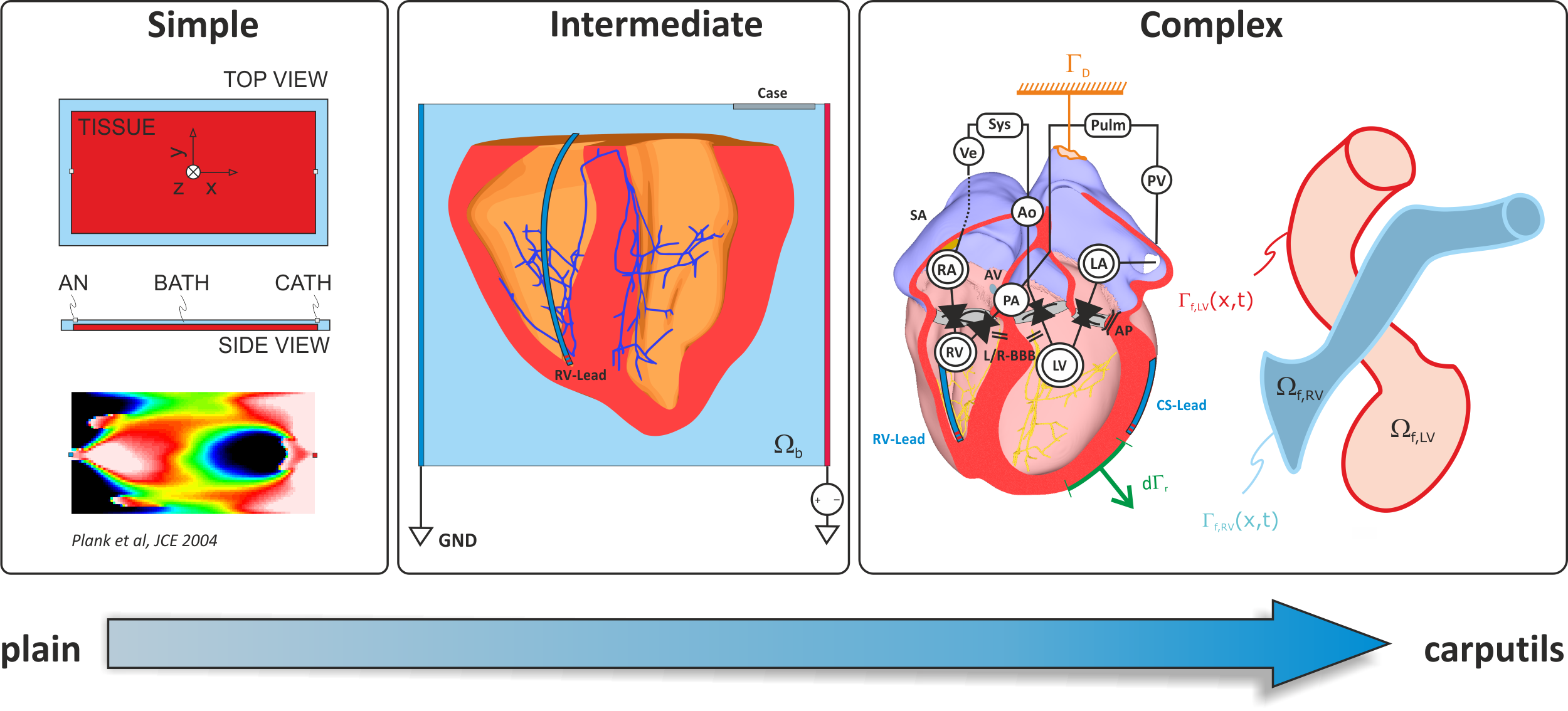
Fig. 2 Complexity of in-silico experiments. Simple experiments are easily managed in plain mode using the simulation tools directly. Experiments of intermediate complexity are also tractable in plain mode, typically scripts are used to organize workflows, but . Complex experiments are not tractable in plain mode. These experiments require careful design and a higher degree of abstraction and workflow automation.